Molecular and Mendelian Genetics - What are the building blocks of life
How exactly do genes in the DNA encode for proteins?
The answer is that the sequence of bases in a gene specifies the sequence of amino acids in the protein. There are four types of bases in the DNA:
• adenine (A)
• cytosine (C)
• guanine (G)
• thymine (T)
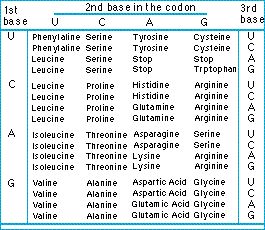
Amino acids are encoded by triplets of bases called codons. The four different bases can be arranged in 64 (4 x 4 x 4) triplets, and each one codes for an amino acid. The relationship between triplet and amino acid has been deciphered and is called the genetic code.
Table: The genetic code. The code is here expressed for mRNA. Each triplet encodes one amino acid. Note that three triplets are stop codons which signal the end of a gene.
| Next |