Classification and evolution - What are the three main schools of classification?
Cladism
Cladism is one of the three main taxonomic schools and is rigorously based upon the phylogenetic principle as a means of biological classification. This means that the cladist’s method is evolutionary: species are grouped according to how recently they share a common ancestor.
When a species splits during evolution it will usually form two descendant species, called sister species, and in a cladistic classification sister species are grouped together.
Cladists therefore ignore phenetic similarities in organisms and attempt to uncover phylogenetic relationships by means of shared derived characters. As a result, they only recognize monophyletic groups: paraphyletic and polyphyletic groups are excluded.
We need to know what these technical terms mean.
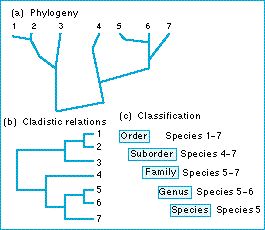
Figure: there is a simple relationship between the phylogenetic (cladistic) classification of a group of species and their phylogenetic tree. (a) The phylogenetic tree of seven species. (b) Their cladistic classification. (c) The formal Linnaean classification, for species five as an example.
| Next |