Transcription
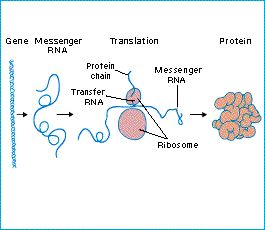
Transcription is the process by which messenger RNA is read off the DNA forming a protein.
In transcription, messenger RNA makes a copy of the DNA and travels to the ribosome (made up of ribosomal RNA) where it is translated into proteins via the transfer RNA. There are 20 kinds of transfer RNA molecules, one for each of the 20 main amino acids. A transfer RNA molecule has an amino acid attatched to it, and contains the anti-codon corresponding to that amino acid in another part of its structure. In protein synthesis, each codon in the messenger RNA combines with appropriate tRNA's anti-codon, and the amino acids are arranged in order to make the protein.
Figure: the transfer of information in the cell.
| Next |