Back
Acta Physiologica 2012; Volume 204, Supplement 689
91st Annual Meeting of The German Physiological Society
3/22/2012-3/25/2012
Dresden, Germany
ENDOTHELIN RECEPTOR INHIBITION AND ITS EFFECTS ON LOX-1 EXPRESSION IN AMIODARONE-INDUCED LUNG FIBROSIS IN RAT
Abstract number: P121
Landsberger1 *M., Schnell2 M., Ewert2 R.
1Institute of Pathophysiology, University Medicine Greifswald, Karlsburg, Germany
2University Medicine Greifswald, Department of Internal Medicine B, Greifswald, Germany
Questions:
Increased expression of endothelin-1 (ET-1) induces chronic inflammation, expression of the receptor for oxidized low density (LDL) lipoprotein, LOX-1, and development of lung fibrosis in transgenic mice. The role of LOX-1 in the development of amiodarone-induced pulmonary fibrosis is unknown.
Methods:
Fibrosis was induced in adult, 6–8 weeks old male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats by intra-tracheal administration of amiodarone (1.83 mmol) followed by dispersion to the alveoli by air jet at baseline and after 48 hours. Bosentan (100 mg/kg) or sitaxentan (5 mg/kg) was administered by gavage daily for seven weeks. Animals (amiodarone plus bosentan or sitaxentan) were pre-treated with bosentan or sitaxentan for three days before administration of amiodarone. The animal study was approved by the localanimal care committee. Total RNA was isolated by standard procedures. LOX-1 and preproET-1 mRNA expressions (mean±standard deviation) were quantified by reverse transcription PCR and corrected for beta-actin expression.
Results:
Amiodarone treatment did not significantly affect preproET-1 expression and LOX-1 expression in lungs and kidneys after 35 days compared to controls but up-regulated preproET-1 (P).
Conclusions:
LOX-1 mRNA expression may not be correlated with amiodarone-induced lung fibrosis in SD rats. However, amiodarone and ET-1 receptor inhibition by bosentan or sitaxentan may act synergistically to up-regulate LOX-1 expression in lung and heart by a yet unknown mechanism.
Table 1. LOX-1 and preproET-1 mRNA expressions after 35 days. Data were analysed by Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni t-test (lung) or Dunn's test (heart). In all cases, P<0.05was considered statistically significant. All data are expressed as group means ± SD. * P<0.05 vs. control, ‡ P<0.05 vs. amiodarone/bosentan, † P<0.05 vs. sitaxsentan.
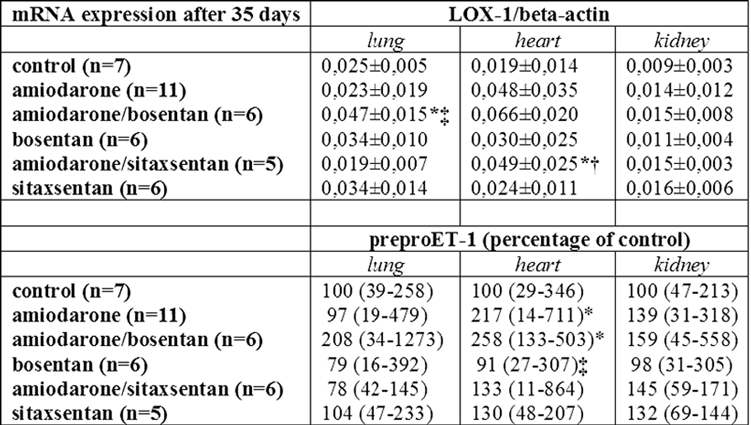
Figure 1
To cite this abstract, please use the following information:
Acta Physiologica 2012; Volume 204, Supplement 689 :P121