Amino acids
Animo acids are the unit molecular building blocks of proteins. A protein is a chain of amino acids in a certain sequence. Twenty main types of amino acid are found in the proteins of living things, and the properties of a protein are determined by its particular amino acid sequence.
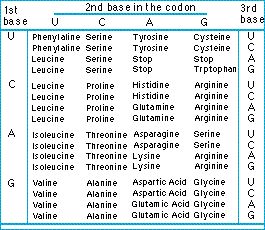
Amino acids are encoded in the DNA by triplets of bases called codons. The four different bases - adenosine, cytosine, thymine and guanine - can be arranged in 64 (4 x 4 x 4) triplets, and each one codes for an amino acid. The relationship between triplet and amino acid has been deciphered and is called the genetic code.
It is possible to estimate the phylogenetic relatedness of two species by inferring their molecular evolution from the differences in amino acids between them.
Figure: the genetic code. The code is here expressed for mRNA. Each triplet encodes one amino acid (notice three triplets are "stop" codons, which signal the end of a gene).
| Next |